- This is the basic hardware that the microprogram will control
- for each ISA instruction, the microprogram will go through the
proper sequence of operations of these hardware elements to
accomplish the task
- access to these hardware elements can only be done at the
microprogram level: ISA cannot manipulate this directly
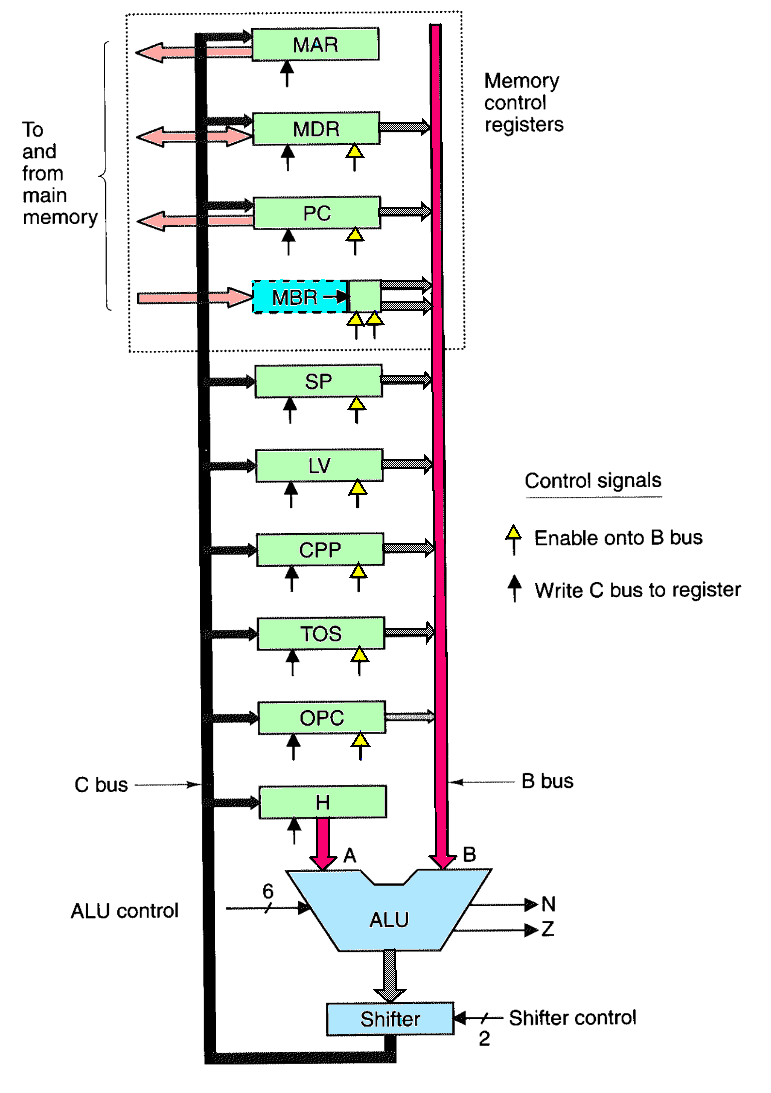
- Buses
- A Bus - Only contents of register H can go on this bus
and it serves as left input of ALU
- B Bus - serves as right input to ALU; most registers can put
their contents on this bus
- C Bus - carries ALU output back into registers
- Registers
- 32 bit registers
- each has one or two control inputs for outputting and loading
the register
- overview (details discussed below)
- MAR - Memory Address register
- MDR - Memory Data Register
- PC - Program Counter
- MBR - Memory Buffer Register
- SP - Stack Pointer
- LV - Local Variable pointer
- CPP - Constant Pool Pointer
- TOS - Top of Stack register
- OPC - OpCode register (mostly a scratch register)
- H - Holding Register is the left ALU input.
- ALU has 6 control lines and two outputs
- shifter has 2 control lines
- not shown are 3 memory control lines
- total of 29 control lines in microarchitecture
|
|

