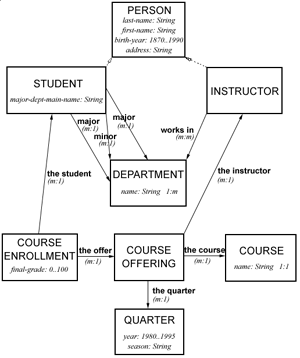
Figure Ref-1. A semantic schema for a university application.
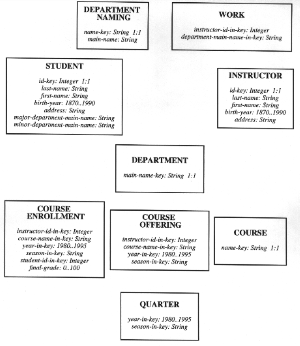
Figure Ref-2. A relational schema for the university
application.
The recent development of the new generation of data models - the semantic models - offers a simple, natural, implementation- independent, flexible, and nonredundant specification of information and its semantic aspects. Since the original idea of [Abrial-74], many semantic data models have been studied in the computer science literature. Many semantic models have been surveyed in [Hull&King-87] and [Peckham&Maryanski-88]. Although somewhat differing in their terminology and their selection of tools used to describe the semantics of the real world, the various semantic models are roughly equivalent and have several common principles:
This book is based on the Semantic Binary Model (SBM) ([Rishe-87-RM],
[Rishe-89-SD], [Rishe-90-SB]), a descendant of the model of [Abrial-
74]. Models similar to SBM have been studied in: [Bracchi&al.-76],
[Nijssen-77], [Nijssen-81], [Breutman&al.-79], [Senko-78], [Mark-83],
[Mark-87], [Mark-89], [Meersman&Assche-83], [Vermeir-83], and others.
SBM does not have as rich an arsenal of tools for semantic description
as can be found in some other semantic models, such as the IFO model
[Abiteboul&Hull-84], SDM [Hammer&McLeod-81], the Functional Model
([Kerschberg&Pacheco-76], [Shipman-81], [Chan&al.-82]), SEMBASE
[King-84], NIAM ([Nijssen-81], [Verheijen&VanBekkum-82],
[Leung&Nijssen-87]), Taxis [Nixon&al.-87], SIM [Jagannathan&al.-88],
SAM [Su&Lo-80], OSAM* [Su-88-OS], GEM [Tsur&Zaniolo-84], GENESIS
[Batory&al.-88], ER [Chen-76]. Nevertheless, the SBM has a small set
of sufficient simple tools by which all of the semantic descriptors of
the other models can be constructed. This makes SBM easier to use for
the novice, easier to implement, and usable for delineation and study
of the common properties of the semantic models.
Typically, semantic data models have been experimentally implemented
as interfaces to database management systems in other data models,
(e.g., the relational or the network model). (Although, there are less
typical, direct implementations, e.g., [Lien&al.-81], [Chan&al.-82],
[Benneworth&al.-81].) The efficiency of an interface implementation
is limited to that of the conventional DBMS and is normally much worse
due to the interface overhead. The direct implementations were
previously believed to be less efficient than the conventional
systems. However, the semantic models have potential for much more
efficient implementation than the conventional data models, as was
shown in [Lin&al.-89], [Rishe-89-EO], and [Rishe-91-FS].
The use of semantic models for the design of relational schemas has
been studied in [Brodie&al.-84-CM], [Chen-76], [King&McLeod-85],
[Teorey&al.-86], [Leung&Nijssen-87], [Shoval/Even-Chaime-87],
[Verheijen&VanBekkum-82], [DeTroyer&Meersman-86], [Shoval-85], and
other works. A graphical interactive system for the design of semantic
databases is discussed in [Shoval&al.-88],
Nonprocedural languages for semantic databases have been studied in
[Meersman-81], [Shipman-81], [Senko-78], [Rishe-86-PS], [Rishe-91-PC],
and others. Extended Pascal for semantic databases is defined in
[Rishe-88-TM]. Data definition languages integrated with data
manipulation languages for semantic databases have been studied in
[Roussopoulos&Mark-85].
[Abiteboul&Hull-84] S. Abiteboul and R. Hull. ``IFO: A Formal Semantic
Database Model,'' Proceedings of ACM SIGACT-SIGMOD Symposium on
Principles of Database Systems, 1984.
[Abrial-74] J.R. Abrial, ``Data Semantics,'' in J.W. Klimbie and K.L.
Koffeman (eds.), Data Base Management. North Holland, 1974.
[Batory&al.-88] D.S. Batory, T.Y. Leung, and T.E. Wise.
``Implementation Concepts for an Extensible Data Model and Data
Language.'' ACM Transactions on Database Systems, vol. 13, no. 3,
September 1988, pp. 231-262.
[Benneworth&al.-81] R.L. Benneworth, C.D. Bishop, C.J.M. Turnbull,
W.D. Holman, F.M. Monette. ``The Implementation of GERM, an
Entity-Relationship Data Base Management System.'' Proceedings of
the Seventh International Conference on Very Large Data Bases.
(C. Zaniolo & C. Delobel, eds.) IEEE Computer Society Press,
1981, pp. 465-477.
[Bracchi&al.-76] G. Bracchi, P. Paolini, G. Pelagatti. ``Binary
Logical Associations in Data Modelings.'' In G.M. Nijssen (ed.),
Modeling in Data Base Management Systems. IFIP Working Conference
on Modeling in DBMSs, 1976.
[Breutman&al.-79] B. Breutman, E. Falkenberg, and R. Mauer. ``CSL: A
Conceptual Schema Language.'' Proceedings IFIP TC 2 WG 2.6
Working Conference, March 1979.
[Brodie&al.-84-CM] M.L. Brodie, J. Mylopoulos, and J.W. Schmidt
(eds.). On Conceptual Modelling. Springer-Verlag, New York,
1984.
[Chan&al.-82] A. Chan, S. Danberg, S. Fox, W. Lin, A. Nori, and D.R.
Ries. ``Storage and Access Structures to Support a Semantic Data
Model.'' Proceedings of the Eighth International Conference on
Very Large Data Bases. IEEE Computer Society Press, 1982.
[Chen-76] P. Chen. ``The Entity-Relationship Model: Toward a Unified
View of Data.'' ACM Trans. Database Syst. 1, 1, pp. 9-36.
[Codd-70] E. Codd. ``A Relational Model for Large Shared Data Banks.''
Communications of ACM, 13:6.
[Codd-71] E. Codd. ``A Data Base Sublanguage Founded on the Relational
Calculus.'' Proceedings of the ACM SIGFIDET Workshop on Data
Description, Access, and Control, ACM, 1971.
[DeTroyer&Meersman-86] O. de Troyer and R. Meersman. ``Transforming
Conceptual Schema Semantics to Relational Database
Applications.'' Fourth Scandinavian Research Seminar on
Information Modeling and Data Base Management, 1986.
[Hammer&McLeod-81] M. Hammer and D. McLeod. ``Database Description
with SDM: A Semantic Database Model,'' ACM Transactions on
Database Systems, vol. 6, no. 3, 1981, pp. 351-386.
[Hull&King-87] R. Hull and R. King. ``Semantic Data Models.'' ACM
Computing Surveys, 20, 3, pp. 153-189.
[Jagannathan&al.-88] D. Jagannathan, R.L. Guck, B.L. Fritchman, J.P.
Thompson, D.M. Tolbert. ``SIM: A Database System Based on
Semantic Model.'' Proceedings of SIGMOD International Conference
on Management of Data. Chicago, June 1-3, 1988. ACM-Press, 1988.
[Kerschberg&Pacheco-76] L. Kerschberg and J.E.S. Pacheco. ``A
Functional Data Base Model.'' Tech. Rep., Pontificia Univ.
Catolica do Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 1976.
[King-84] R. King. ``SEMBASE: A Semantic DBMS.'' Proceedings of the
First Workshop on Expert Database Systems. Univ. of South
Carolina, 1984, pp. 151-171.
[King&McLeod-85] R. King and D. McLeod. ``A Database Design
Methodology and Tool for Information Systems.'' ACM Transactions
on Office Information Systems, 3, 1, pp. 2-21.
[Leung&Nijssen-87] C.M.R. Leung and G.M. Nijssen. ``From a NIAM
Conceptual Schema into the Optimal SQL Relational Database
Schema.'' Aust. Comput. J., vol. 19, no. 2.
[Lien&al.-81] Y.E. Lien, J.E. Shopiro, S. Tsur. ``DSIS - A Database
System with Interrelational Semantics.'' Proceedings of the
Seventh International Conference on Very Large Data Bases. (C.
Zaniolo & C. Delobel, eds.) IEEE Computer Society Press, 1981, pp
465-477.
[Lin&al.-89] C. Lin, L. Mark, T. Sellis, and C. Faloutsos. ``Query
Optimization in the Binary Relationship Model.'' Data and
Knowledge Engineering. September 1989, pp. 195-221.
[Mark-83] L. Mark. ``What Is Binary Relationship Approach?'' Entity-
Relationship Approach to Software Engineering. North-Holland,
1983.
[Mark-87] L. Mark. ``Defining Views in the Binary Relationship
Model.'' Information Systems, vol. 12, no. 3, 1987.
[Mark-89] L. Mark. ``A Graphical Query Language for the Binary
Relationship Model'' Information Systems, vol. 14, no. 3, 1989.
[Meersman-81] R. Meersman. ``RIDL: A Query System as Support for
Information Analysis.'' ECODO 32, September 1981.
[Meersman&Assche-83] R. Meersman and F. Van Assche. ``Modeling and
Manipulating Production Data Bases in Terms of Semantic Nets.''
8th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence,
Karlsruhe, 1983, pp. 325-329.
[Nijssen-77] G.M. Nijssen. ``Current Issues in Conceptual Schema
Concepts.'' Architecture and Models in Data Base Management
Systems North-Holland, 1977.
[Nijssen-81] G.M. Nijssen ``An architecture for knowledge base
systems,'' Proceedings, SPOT-2 Conference, Stockholm, 1981.
[Nixon&al.-87] B. Nixon, L. Chung, I. Lauzen, A. Borgida, and M.
Stanley. ``Implementation of a Compiler for a Semantic Data
Model: Experience with Taxis.'' In Proceedings of the ACM SIGMOD
Conference ACM, 1987.
[Peckham&Maryanski-88] J. Peckham and F. Maryanski. ``Semantic
Database Modeling: Survey, Applications, and Research Issues.''
ACM Computing Surveys, 19, 3, pp. 201-260.
[Rishe-86-PS] N. Rishe. ``Postconditional Semantics of Data Base
Queries.'' Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 239
(Mathematical Foundations of Programming Semantics. A. Melton,
ed.), Springer-Verlag, 1986, pp. 275-295.
[Rishe-87-RM] N. Rishe. ``On Representation of Medical Knowledge by a
Binary Data Model.'' Journal of Mathematical and Computer
Modelling, vol. 8 (1987), pp. 623-626.
[Rishe-88-TM] N. Rishe. ``Transaction-Management System in a Fourth-
Generation Language for Semantic Databases.'' In: Mini and
Microcomputers: From Micros to Supercomputers (Proceedings of the
ISMM International Conference on Mini and Microcomputers, Miami
Beach, December 14-16, 1988; M.H. Hamza, ed.), Acta Press, 1988,
pp. 92-95.
[Rishe-89-EO] N. Rishe. ``Efficient Organization of Semantic
Databases'' Foundations of Data Organization and Algorithms.
(FODO-89) W. Litwin and H.-J. Schek, eds. Springer-Verlag
Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 367, pp. 114-127, 1989.
[Rishe-89-SD] N. Rishe. ``Semantic Database Management: From
Microcomputers to Massively Parallel Database Machines.'' Keynote
Paper, Proceedings of the Sixth Symposium on Microcomputer and
Microprocessor Applications, Budapest, October 17-19, 1989, pp
1-12.
[Rishe-90-SB] N. Rishe. ``Semantic Binary Database Model.'' HK
Computer Journal, 6, 11 (1990), pp. 30-34.
[Rishe-91-FS] N. Rishe. ``A File Structure for Semantic Databases.''
Information Systems, 16, 4 (1991), pp. 375-385.
[Rishe-91-PC] N. Rishe and W. Sun. ``A Predicate Calculus Language
for Queries and Transactions in Semantic Databases.'' In:
Databases: Theory, Design and Applications. IEEE Computer Society
Press, 1991 (N. Rishe, S. Navathe, and D. Tal, eds.) pp. 204-
221.
[Roussopoulos&Mark-85] N. Roussopoulos and L. Mark. ``Schema
Manipulation in Self-Describing and Self-Documenting Data
Models.'' International Journal of Computer and Information
Sciences, vol.14, no.1, 1985.
[Senko-78] M.F. Senko. ``Foral LP: Design and Implementation.''
Proceedings of Very Large Data Base Conference, 1978.
[Shipman-81] D.W. Shipman. ``The Functional Data Model and the Data
Language DAPLEX.'' ACM Transactions on Database Systems, vol. 6,
no. 1, pp. 140-173, 1981.
[Shoval-85] P. Shoval. ``Essential Information Structure Diagrams and
Database Schema Design.'' Information Systems, vol. 10, no. 4,
1985.
[Shoval&al.-88] P. Shoval, E. Gudes, and M. Goldstein. ``GISD: A
Graphical Interactive System for Conceptual Database Design.''
Information Systems, vol. 13, no.1, 1988.
[Shoval/Even-Chaime-87] P. Shoval and M. Even-Chaime. ``ADDS: A
Systems for Automatic Database Schema Design Based on the
Binary-Relationship Model.'' Data and Knowledge Engineering 2,
1987.
[Su-88-OS] S. Su. ``An Object-Oriented Semantic Association Model
(OSAM*) for CAD/CAM Databases.'' In: AI in Industrial Engineering
and Manufacturing: Theoretical Issues and Applications (Soyster
and Kashyap, eds.), 1988.
[Su&Lo-80] S.Y.W. Su and D.H. Lo. ``A Semantic Association Model for
Conceptual Database Design.'' In: P.P. Chen (ed.), Entity-
Relationship Approach to Systems Analysis and Design, North-
Holland, Amsterdam, 1980, pp. 147-171.
[Teorey&al.-86] T.J. Teorey, D. Yang, and J.P. Fry. ``A Logical Design
Methodology for Relational Databases using the Extended Entity-
Relationship Model.'' ACM Computing Surveys, 18, 2, pp. 197-222.
[Tsur&Zaniolo-84] S. Tsur and C. Zaniolo. ``An Implementation of GEM -
Supporting a Semantic Data Model on a Relational Backend.'' In:
Proceedings of ACM SIGMOD Intl. Conference on Management of Data,
May 1984.
[Verheijen&VanBekkum-82] G.M.A. Verheijen and J. Van Bekkum. ``NIAM -
An Information Analysis Method,'' In: Information Systems Design
Methodologies: A Comparative Review, T.W. Olle et al., eds.,
IFIP, North-Holland, 1982.
[Vermeir-83] D. Vermeir. ``Semantic Hierarchies and Abstraction in
Conceptual Schemata'' Information Systems, vol.8, no.2, 1983.
12.2. General Database Bibliography
ACM. Proceedings of the 1989 ACM SIGMOD International Conference on
the Management of Data, Portland, Oregon. Baltimore, MD:
Association of Computing Machinery, 1989.
ACM. Proceedings of the Eighth ACM SIGACT-SIGMOD-SIGART Symposium on
Principles of Database Systems, March 29-31, 1989, Philadelphia,
Pennsylvania. Baltimore, MD: Association of Computing Machinery,
1989.
ACM. Proceedings of the Ninth ACM SIGACT-SIGMOD-SIGART Symposium on
Principles of Database Systems, April 2-4, 1990, Nashville,
Tennessee. Baltimore, MD: Association of Computing Machinery,
1990.
ACM. Proceedings of the Sixth ACM SIGACT-SIGMOD-SIGART Symposium on
Principles of Database Systems, March 23-25, 1987, San Diego,
California. Baltimore, MD: Association of Computing Machinery,
1987.
ACM. Proceedings, Second International Symposium on Databases in
Parallel and Distributed Systems: July 2-4, 1990, Trinity
College, Dublin, Ireland. Baltimore, MD: Association of Computing
Machinery, 1990.
ACM. SIGIR 89: Proceedings of the Twelfth Annual International
ACMSIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information
Retrieval, Cambridge, Massachusetts, U.S.A., June 25-28, 1989.
Baltimore, MD: Association of Computing Machinery, 1989.
Abiteboul, S., P.C. Fischer, H.J. Schek. Nested relations and complex
objects in databases. Berlin; New York: Springer-Verlag, 1989.
Abiteboul, S., P.C. Kanellakis (edit.) ICDT 90: Third International
Conference on Database Theory, Paris, France, December 12-14,
1990: proceedings. Berlin; New York: Springer-Verlag, 1990.
Alagic, Suad. Object-oriented database programming. New York:
Springer-Verlag, 1989.
Andersen, Dick, Bill Weil. 1-2-3 database techniques. Carmel, IN: Que
Corp., 1989.
Armenskii, A.E. Tenzornye metody postroeniia informatsionnykh sistem.
Moskva: Nauka, 1989.
Atkinson, Malcolm P., Peter Buneman, Ronald Morrison (edit.) Data
types and persistence. Berlin; New York: Springer-Verlag, 1988.
Atre, Shaku. Data base: structured techniques for design,
performance, and management. 2d ed. New York: Wiley, 1988.
Austing, Richard H., Lillian N. Cassel. File organization and access,
from data to information. Lexington, MA: DC Heath, 1988.
Bagchi, Tapan P., Vinay K. Chaudhri. Interactive relational database
design: a logic programming implementation. Berlin; New York:
Springer-Verlag, 1989.
Bancilhon, Francois, Peter Buneman (edit.) Advances in database
programming languages. New York, NY: ACM Press: Reading, MA:
Addison-Wesley, 1990.
Barker, Richard. CASE*Method: entity relationship modelling.
Wokingham, England: Reading, MA: Addison-Wesley, 1990.
Barker, Richard. CASE*Method: tasks and deliverables. Wokingham,
England: Reading, MA: Addison-Wesley, 1990.
Batini, C., S. Ceri, and S.B. Navathe. Database design: an entity
relationship approach. Benjamin-Cummings, 1990.
Batini, Carlo (edit.) Entity-relationship approach: a bridge to the
user: proceedings of the Seventh International Conference on
Entity-Relationship Approach, Rome, Italy, November 16-18, 1988.
Amsterdam; New York: North-Holland; New York, NY: Elsevier, 1989.
Beeri, C., J.W. Schmidt, U. Dayal (edit.) Proceedings of the Third
International Conference on Data and Knowledge Bases - Improving
Usability and Responsiveness: June 28-30, 1988, Jerusalem,
Israel. San Matheo, CA: Morgan Kaufmann, 1988.
Benson, James A., Bella Hass Weinberg (edit.) Gateway software and
natural language interfaces: options for online searching. Ann
Arbor, MI: Pierian Press, 1988.
Benyon, David. Information and data modelling. Oxford; Boston:
Blackwell Scientific Publications: Brookline Village, MA:
Distributors, U.S.A., Publishers' Business Services, 1990.
Bernstein, Philip A., Vassos Hadzilacos, Nathan Goodman. Concurrency
control and recovery in database systems. Reading, MA: Addison-
Wesley, 1987.
Bielawski, Larry, Robert Lewand. Intelligent systems design: expert
systems, hypermedia, and database technologies. New York: Wiley,
1991.
Birrell, Andrew D., Michael B. Jones, and Edward P. Wobber. A simple
and efficient implementation for small databases. Palo Alto, CA:
Digital Systems Research Center, 1988.
Biskup, J., et al. MFDBS 87: 1st Symposium on Mathematical
Fundamentals of Database Systems, Dresden, GDR, January 19-23,
1987: proceedings. Berlin; New York: Springer-Verlag, 1988.
Blaser, A. (edit.) Database systems of the 90s: international
symposium, Muggelsee, Berlin, FRG, November 5-7, 1990:
proceedings. Berlin; New York: Springer-Verlag, 1990.
Boisgontier, J., and C. Donay. File handling in Turbo Pascal. London:
Paradigm, 1988.
Boral, H., P. Faudemay (edit.) Database machines: sixth international
workshop, IWDM 89, Deauville, France, June 19-21, 1989:
proceedings. Berlin; New York: Springer-Verlag, 1989.
Brackett, Michael H. Developing data structured databases. Englewood
Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall, 1987.
Brackett, Michael H. Practical data design. Englewood Cliffs, NJ:
Prentice Hall, 1990.
Braithwaite, Kenmore S. Database management and control. New York:
Intertext Publications: McGraw-Hill, 1990.
Brathwaite, Kenneth S. Analysis, design, and implementation of data
dictionaries. New York: McGraw-Hill, 1988.
Brathwaite, Kenneth S. Systems design in a database environment. New
York: Intertext Publications: McGraw-Hill, 1989.
Brathwaite, Kenneth S. The data base environment: concepts and
applications. New York: Van Nostrand, 1990.
Burns, George. Database applications in engineering. Wilmslow: Sigma,
1989.
Cabrera, Luis-Felipe, and Darrell D.E. Long. Swift: a storage
architecture for very large objects. Santa Cruz, CA: University
of California, Santa Cruz, Computer Research Laboratory, 1989.
Cardenas, A., and D. McLeod (edit.) Research foundations in object-
oriented and semantic database systems. Englewood Cliffs, NJ:
Prentice-Hall, 1990.
Ceri, S., G. Gottlob, L. Tanca. Logic programming and databases.
Berlin; New York: Springer-Verlag, 1990.
Cesarini, Francesca, and Silvio Salza (edit.) Database machine
performance: modeling methodologies and evaluation strategies.
Berlin; New York: Springer-Verlag, 1987.
Chorafas, Dimitris N. Handbook of database management and distributed
relational databases. 1st ed. Blue Ridge Summit, PA: TAB Books,
1989.
Cobb, Douglas, and Jeff Yocom, et al. Douglas Cobb's Paradox 3
handbook. 2d ed. New York: Bantam Books, 1989.
Cobb, Stephen. Using Reflex: the database manager. Berkeley, CA:
Osborne McGraw-Hill, 1987.
Codd, E.F. The relational model for database management: version 2.
Reading, MA: Addison-Wesley, 1990.
Condliffe, Susa. Paradox: a business user's guide. New York: Wiley,
1989.
Cronin, Daniel J. Mastering ORACLE: featuring ORACLE's SQL standard.
1st ed. Indianapolis, IN, U.S.A.: Hayden Books, 1988, 1989.
Date, C.J. Relational database writings 1985-1989. Reading, MA:
Addison-Wesley, 1990.
Date, C.J. A guide to INGRES: a user's guide to the INGRES product
from Relational Technology Inc. Reading, MA: Addison-Wesley,
1987.
Date, C.J. A guide to the SQL standard: a user's guide to the
standard relational language SQL. 2d ed. Reading, MA: Addison-
Wesley, 1989.
Date, C.J., and Colin J. White. A guide to DB2. 3d ed. Reading, MA:
Addison-Wesley, 1989.
Date, C.J., and Colin J. White. A guide to SQL/DS. Reading, MA:
Addison-Wesley, 1989.
Dayal, Umeshwar, and Irv Traiger (edit.) Proceedings of Association
for Computing Machinery Special Interest Group on Management of
Data: 1987 Annual Conference San Francisco May 27-29, 1987. New
York: Association for Computing Machinery, 1987.
DeMaria, Rusel, and Gregory B. Salcedo. Elementary Paradox. Radnor,
PA: Compute! Books, 1990.
DeVita, Joseph. The database experts' guide to FOCUS. New York, NY:
Intertext Publications: McGraw-Hill, 1988.
Debenham, John K. Knowledge systems design. Englewood Cliffs, NJ:
Prentice Hall, 1989.
Deen, S.M., G.P. Thomas (edit.) Data & knowledge base integration.
London: Pitman, 1990.
Deen, S.M., G.P. Thomas (edit.) Data and knowledge base integration:
proceedings of the Working Conference on Data and Knowledge Base
Integration held at the University of Keele, England on October
4-5, 1989. London: Pitman, 1990.
Demetrovics, J., B. Thalheim (edit.) MFDBS 89: 2d Symposium on
Mathematical Fundamentals of Database Systems, Visegrad, Hungary,
June 26-30, 1989: proceedings. Berlin; New York: Springer-Verlag,
1989.
Desai, Bipin C. An introduction to database systems. West
Publishing Co., 1990.
Diener, Andreas R. An architecture for distributed databases on
workstations. Zurich: Verlag der Fachvereine, 1987.
Dittrich, K.R. (edit.) Advances in object-oriented database systems:
2d International Workshop on Object-oriented Database Systems,
Bad Munster am Stein-Ebernburg, FRG, September 27-30, 1988,
proceedings. Berlin; New York: Springer-Verlag, 1988.
Downes, P.M. Practical data analysis. London: Blenheim, 1989.
Dunlop, Neil. Working with Q & A: practical techniques in database
design. Glenview, IL: Scott, Foresman, 1987.
Dutka, Alan F., Howard H. Hanson. Fundamentals of data normalization.
Reading, MA: Addison-Wesley, 1989.
Eliassen, Frank, Jari Veijalainen. An S-transaction definition
language and execution mechanism. Sankt Augustin: Gesellschaft
fur Mathematik und Datenverarbeitung, 1987.
Elmasri, Ramez, Shamkant B. Navathe. Fundamentals of database
systems. Redwood City, CA: Benjamin/Cummings, 1989.
Fabbri, Tony, A. Robert Schwab, Jr. Working with DB2, SQL/DS, SQL,
and QMF. 1st ed. Blue Ridge Summit, PA: TAB Books, 1990.
Fidel, Raya. Database design for information retrieval: a conceptual
approach. New York: Wiley, 1987.
Finkelstein, Clive. An introduction to information engineering: from
strategic planning to information systems. Sydney; Reading, MA:
Addison-Wesley, 1989.
Fitch, Carl, Charles Hinchey, James Larson. DB2 applications
development handbook. New York: Intertext Publications: McGraw-
Hill, 1989.
Fleming, Candace C., Barbara von Halle. Handbook of relational
database design. Reading, MA: Addison-Wesley, 1989.
Fong, Elizabeth N., and Bruce K. Rosen. Guide to distributed database
management. Gaithersburg, MD: U.S. Dept. of Commerce, National
Bureau of Standards: Washington, DC: For sale: the Supt. of
Docs., US GPO., 1988.
Fosdick, Howard. OS/2 database manager: a developer's guide. New
York: Wiley, 1989.
Fosdick, Howard. The best book of OS/2 database manager. 1st ed.
Indianapolis, IN: Hayden Books, 1989.
Frank, Lars. Database: theory and practice. Workingham, England:
Reading, MA: Addison-Wesley, 1988.
Gardarin, Georges, Patrick Valduriez. Relational databases and
knowledge bases. Reading, MA: Addison-Wesley, 1989.
Gaydasch, Alexander, Jr. Effective database management. Englewood
Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall, 1988.
Geller, Joseph R. IMS administration, programming, and data base
design. New York: J Wiley, 1989.
Ghosh, Sakti P., Yahiko Kambayashi, and Katsumi Tanaka (edit.)
Foundations of data organization. New York: Plenum Press, 1987.
Gillenson, Mark L. Database: step-by-step. 2d ed. New York: Wiley,
1990.
Gilor, Dov. SQL/DS performance: techniques for improvement. New York:
Wiley, 1991.
Ginsberg, Allen. Automatic refinement of expert system knowledge
bases. London: Pitman: San Mateo, CA: Morgan Kaufmann, 1988.
Goley, George F., I.V. Dynamics of FoxBASE+ programming. Homewood,
IL: Dow Jones-Irwin, 1988.
Grant, John. Logical introduction to databases. San Diego: Harcourt
Brace Jovanovich, 1987.
Gray, W.A. (edit.) Proceedings of the Sixth British National
Conference on Databases. Cambridge: New York: Cambridge
University Press on behalf of the British Computer Society, 1988.
Gunther, Oliver. Efficient structures for geometric data management.
Berlin; New York: Springer-Verlag, 1988.
Gupta, Amar (edit.) Integration of information systems: bridging
heterogeneous databases. New York: IEEE Press, 1989.
Gupta, R., and E. Horowitz (edit.) Object-oriented databases with
applications to CASE, networks, and VLSI CAD. Englewood
Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall, 1990.
Gyssens, M., J. Paredaens, D. Van Gucht. ICDT 88: 2d International
Conference on Database Theory, Bruges, Belgium, August 31-
September 2, 1988: proceedings. Berlin; New York: Springer-
Verlag, 1988.
Hansen, Gary W. Database processing with fourth generation languages.
Cincinnati, OH: South-Western, 1988.
Harrington, Jan L. Database management with Double Helix 3.0. New
York: Brady: Distributed Prentice Hall Trade, 1990.
Harrington, Jan L. Database management with Double Helix II for the
Macintosh and VAX. New York: Brady: Distributed Prentice Hall
Trade, 1988.
Hartman, Patricia A., Cary N. Prague, and James E. Hammitt. Paradox
programming. 1st ed. Blue Ridge Summit, PA: Windcrest, 1991.
Hawryszkiewcz, Igor Titus. The art of database design. New York:
Macmillan, 1990.
Hennerkes, Wilhelm A. MAXDATA: a time series data base system.
Berlin; New York: Springer-Verlag, 1990.
Heydt, Robert, and Diane Heydt. DB2 database design and
administration: version 2. New York: Wiley, 1989.
Hinterberger, Hans. Data density: a powerful abstraction to manage
and analyze multivariate data. Zurich: Verlag der Fachvereine,
1987.
Hixson, Amanda C. Rapidfile for business users. Toronto; New York:
Bantam, 1987.
Hoechst, Tim, Nicole Melander, Christopher Chabris. Guide to ORACLE.
New York: Intertext Publications: McGraw-Hill, 1990.
Holloway, Simon. Data administration. Aldershot, Hants, England:
Gower Technical Press: Brookfield, VT: Gower, 1988.
Howe, D.R. Data analysis for data base design. 2d ed. London; New
York: E Arnold: New York, NY: Distributed in the U.S.A.
Routledge, Chapman, and Hall, 1989.
Hughes, John G. Database technology: a software engineering approach.
Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall, 1988.
Hull, Richard, Ron Morrison, David Stemple. Proceedings of the Second
International Workshop on Database Programming Languages, June
4-8, 1989 Salishan Lodge, Gleneden, Beach, Oregon. San Mateo, CA:
Morgan Kaufmann, 1989.
Hursch, Carolyn J., and Jack L. Hursch. SQL, the structured query
language. 1st ed. Blue Ridge Summit, PA: TAB Books, 1988.
Hurson, A.R., L.L. Miller, and S.H. Pakzad. Tutorial: parallel
architectures for database systems. Washington, DC: IEEE Computer
Society Press: Los Angeles, CA: Order from IEEE Computer Society,
1989.
IEEE. Data engineering: proceedings of the Fifth International
Conference on Data Engineering, February 6-10, 1989, Los Angeles,
California, U.S.A. Washington, DC: IEEE Computer Society Press,
1989.
IEEE. Data engineering: proceedings of the Fourth International
Conference on Data Engineering, February 1-5, 1988, Los Angeles
Airport Hilton and Towers, Los Angeles, California, U.S.A.
Washington, DC: Computer Society Press of the IEEE: Los Angeles,
CA:
IEEE. Proceedings, Third International Conference on Data
Engineering, February 3-5, 1987, Pacifica Hotel, Los Angeles,
California U.S.A. Washington, DC: IEEE Computer Society Press:
1987.
Inmon, W.H. Advanced topics in information engineering. Wellesley,
MA: QED Information Sciences, 1989.
Inmon, W.H. Information engineering for the practitioner: putting
theory into practice. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall, 1988.
Inmon, W.H. ORACLE: building high performance online systems.
Wellesley, MA: QED Information Sciences, 1989.
Inmon, W.H. Optimizing performance in DB2 software. Englewood Cliffs,
NJ: Prentice Hall, 1988.
Inmon, W.H. Using DB2 to build decision support systems. Wellesley,
MA: QED Information Sciences, 1990.
Ivanov, I.U.N. Teoriia informatsionnykh obektov i sistemy upravleniia
bazami dannykh. Moskva: Nauka, Glav. red. fiziko-matematicheskoi
lit-ry, 1988.
Jackson, Glenn A. Relational database design with microcomputer
applications. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall, 1988.
Jones, Edward. Paradox. Berkeley, CA: Osborne McGraw-Hill, 1988.
Jones, Paul E., Robert M. Curtice. Logical data base design. 2d ed.
Wellesley, MA: QED Information Sciences, 1988.
Kamin, Jonathan. The first book of Paradox 3. 1st ed. Carmel, IN:
Sams, 1990.
Keogh, James. Paradox 3: the complete reference. Berkeley:
Osborne/McGraw-Hill, 1989.
Keogh, James. Paradox: the complete reference. Berkeley, CA: Osborne
McGraw-Hill, 1988.
Kerry, Ruth. Integrating knowledge-based and database management
systems. New York: Published on behalf of Central Computer and
Telecommunications Agency Ellis Horwood, 1990.
Kerschberg, Larry (edit.) Proceedings from the First International
Conference on Expert Database Systems. Menlo Park, CA:
Benjamin/Cummings, 1987.
Kerschberg, Larry (edit.) Proceedings from the Second International
Conference on Expert Database Systems. Redwood City, CA:
Benjamin/Cummings, 1989.
Kitagawa, H., T.L. Kunii. The unnormalized relational data model: for
office form processor design. Tokyo; New York: Springer-Verlag,
1989.
Kitsuregawa, Masaru, Hidehiko Tanaka (edit.) Database machines and
knowledge base machines. Boston: Kluwer Academic, 1988.
Kliewer, Bradley D. Guide to Paradox 386. New York: Intertext
Publications: McGraw Hill, 1989.
Knight, Tim. 4th dimension: a complete guide to database development.
Glenview, IL: Scott, Foresman, 1989.
Kotz, Angelika M. Triggermechanismen in Datenbanksystemen. Berlin;
New York: Springer-Verlag, 1989.
Kroenke, David M., Kathleen A. Dolan. Database processing:
fundamentals, design, implementation. 3d ed. Chicago: Science
Research Associates, 1988.
Kunii, Hideko S. Graph data model and its data language. Tokyo; New
York: Springer-Verlag, 1990.
Larson, Bruce L. The database experts' guide to Database 2. New York,
NY: Intertext Publications: McGraw-Hill, 1988.
Larson, James A. (edit.) Tutorial - database management. Washington,
DC: IEEE Computer Society Press: 1987.
Law, Margaret Henderson. Guide to information resource dictionary
system applications: general concepts and strategic systems
planning. Gaithersburg, MD: U.S. Dept. of Commerce, National
Bureau of Standards, 1988.
Lenat, D., and R.V. Guha. Building large knowledge-based systems.
Reading, MA: Addison-Wesley, 1990.
Li, Deyi, and Dongbo Liu. A fuzzy PROLOG database system. Taunton,
Somerset, England: Research Studies Press; New York: Wiley, 1990.
Lim, Pacifico Amarga. DB2 for application programmers. Englewood
Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall, 1990.
Litton, Gerry M. Introduction to database management: a practical
approach. Dubuque, Iowa: WC Brown, 1987.
Litton, Gerry. Understanding Professional file. San Francisco: Sybex,
1990.
Litwin, W., H.J. Schek (edit.) Foundations of data organization and
algorithms: 3d international conference, FODO 1989, Paris,
France, June 21-23, 1989: proceedings. Berlin; New York:
Springer-Verlag, 1989.
Lochovsky, Frederick H. (edit.) Entity-relationship approach to
database design and querying: proceedings of the Eighth
International Conference on Entity-Relationship Approach,
Toronto, Canada, 18-20 October 1989. Amsterdam; New York: North-
Holland; New York: Distributors for the U.S. and Canada,
Elsevier, 1990.
Loomis, Mary E.S. Data management and file structures. 2d ed.
Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall, 1989.
Loomis, Mary E.S. The database book. New York: Macmillan; London:
Collier Macmillan, 1987.
Lorie, Raymond A., Jean-Jacques Daudenarde. SQL and its applications.
Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall, 1991.
Lucas, Robert. Database applications using Prolog. Chichester, West
Sussex, England: E. Horwood; New York: Halsted Press, 1988.
Lusardi, Frank. The database experts' guide to SQL. New York, NY:
Intertext Publications/Multiscience Press: McGraw-Hill, 1988.
Lyon, Lockwood. The IMS/VS expert's guide. New York: Van Nostrand
Reinhold, 1990.
Lyon, Lockwood. The database expert's guide to IMS. New York: Van
Nostrand Reinhold, 1990.
Maciaszek, L.A. Database design and implementation. Englewood Cliffs,
NJ: Prentice Hall, 1990.
Malamud, Carl. INGRES: tools for building an information
architecture. New York: Van Nostrand Reinhold, 1989.
Martin, Charles Fontaine. User-centered requirements analysis.
Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall, 1988.
Martin, James, and Joe Leben. Strategic information planning
methodologies. 2d ed. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall, 1989.
Martin, James, Kathleen Kavanagh Chapman, and Joe Leben. DB2,
concepts, design, and programming. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice
Hall, 1989.
Martin, James, Richard Derer, and Joe Leben. IDMS/R: concepts,
design, and programming. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall,
1990.
Martin, Tim, and Tim Hartley. DB2/SQL: a professional programmer's
guide. New York: Intertext: McGraw-Hill, 1989.
McClelland, Trish. Dynamics of Reflex. Homewood, IL: Dow Jones-Irwin,
1987.
McFadden, Fred R., Jeffrey A. Hoffer. Database management. 3d ed.
Redwood City, CA: Benjamin/Cummings, 1991.
McNichols, Charles W., Sara F. Rushinek. Data base management: a
microcomputer approach. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall,
1988.
Meersman, R.A., A.C. Sernadas (edit.) Data and knowledge, Albufeira,
Portugal, November, 3-7, l986. Amsterdam; New York: North-
Holland; New York: Elsevier, 1988.
Meersman, Robert A., Zhongzhi Shi, Chen-Ho Kung (edit.) Artificial
intelligence in databases and information systems: proceedings of
the IFIP TC2/TC8/WG2.6/WG8.1 Working Conference on the Role of
Artificial Intelligence in Databases and Information Systems,
Guangzhou, PR China, July 4-8, 1988. Amsterdam; New York: North-
Holland; Distributors for the U.S. and Canada: Elsevier, 1990.
Montgomery, Stephen L. Relational database design and implementation
using DB2. New York: Van Nostrand Reinhold, 1990.
Mounsey, Helen (edit.) Building databases for global science: the
proceedings of the first Meeting of the International
Geographical Union Global Database Planning Project, held at
Tylney Hall, Hampshire, UK, May, 9-13, 1988. London: New York:
Taylor & Francis, 1988.
Mount, Ellis (edit.) End-user training for sci-tech databases. New
York: Haworth Press, 1990.
Murdoch, S., and L. Johnson. Intelligent data handling. 1st ed.
London: New York: Chapman and Hall, 1990.
Mylopolous, John, and Michael L. Brodie (edit.) Readings in
artificial intelligence and databases. San Mateo, CA: M Kaufmann,
1989.
NBS. Guideline on functional specifications for database management
systems.. Gaithersburg, MD: U.S. Dept. of Commerce/National
Bureau of Standards; Springfield, VA: National Technical
Information Service, 1987.
Naqvi, Shamim, Shalom Tsur. A logical language for data and knowledge
bases. New York: Computer Science Press, 1989.
Narayan, Rom. Data dictionary: implementation, use, and maintenance.
Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall, 1988.
Nath, Aloke. The guide to SQL Server. Reading, MA: Addison-Wesley,
1990.
Newton, Judith J. Guide on data entity naming conventions.
Gaithersburg, Md. U.S. Dept. of Commerce, National Bureau of
Standards. For sale the Supt. of Docs., USGPO., 1987.
Newton, Judith, Frankie E. Spielman (edit.) Data administration
management and practice: proceedings of the first DAMA Symposium.
Gaithersburg, Md. National Institute of Standards and Technology,
1988.
Nijssen, G.M., T.A. Halpin. Conceptual schema and relational database
design: a fact oriented approach. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice
Hall, 1989.
Ozkarahan, Esen. Database management: concepts, design, and practice.
Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall, 1990.
Ozsu, M.T., and P. Valduriez. Principles of distributed database
systems. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall, 1991.
Page, A.J. Relational databases: concepts, selection, and
implementation. Wilmslow: Sigma, 1990.
Papazoglou, M., and W. Valder. Relational database management: a
systems programming approach. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice
Hall, 1989.
Paredaens, J. (edit.) Databases. London; Orlando: Academic Press,
1987.
Paredaens, Jan, et al. The structure of the relational database
model. Berlin; New York: Springer-Verlag, 1989.
Parsaye, Kamran, et al. Intelligent databases: object-oriented,
deductive hypermedia technologies. New York: Wiley, 1989.
Peinl, Peter. Synchronisation in zentralisierten Datenbanksystemen:
Algorithmen, Realisierungsmoglichkeiten und quantitative Analyse.
Berlin; New York: Springer-Verlag, 1987.
Perry, William E. A standard for auditing computer applications.
Pennsauken, NJ: Auerbach, 1988.
Piggott, Stephen. CICS: a practical guide to system fine tuning. New
York: Intertext Publications: McGraw-Hill, 1989.
Prague, Cary N., James E. Hammitt, and Mark R. Nowacki. Programming
with Paradox. 1st ed. Blue Ridge Summit, PA: TAB Books, 1987.
Pratt, Philip J., Joseph J. Adamski. Database systems: management and
design. Boston: Boyd & Fraser, 1987.
Rada, Roy. HYPERTEXT: from Text to Expertext. 1990.
Rafanelli, M., J.C. Klensin, P. Svensson (edit.) Statistical and
scientific database management: Fourth International Working
Conference SSDBM, Rome, Italy, June 21-23, 1988: proceedings.
Berlin; New York: Springer-Verlag, 1989.
Ranade, Jay, et al. DB2 - concepts, programming, and design. New
York: McGraw-Hill, 1991.
Ricardo, Catherine M. Database systems: principles, design, and
implementation. New York: Macmillan; London: Collier Macmillan,
1990.
Rishe, N., S. Navathe, and D. Tal (edit.) Databases: theory, design
and applications. IEEE Computer Society Press, 1991.
Rishe, N., S. Navathe, and D. Tal (edit.) Proceedings of the
PARBASE-90: International Conference on Databases, Parallel
Architectures, and their Applications. IEEE Computer Society
Press, 1990.
Rodgers, Ulka. UNIX database management systems. Englewood Cliffs,
NJ: Prentice Hall, 1990.
Rolland, C., F. Bodart, M. Leonard (edit.) Temporal aspects in
information systems: proceedings of the IFIP TC 8/WG 8.1 Working
Conference on Temporal Aspects in Information Systems, Sophia-
Antipolis, France, May, 13-15, 1987. Amsterdam; New York: North
Holland; New York: Elsevier, 1988.
Rolland, Fr (edit.) Relational database management with Oracle.
Reading, MA: Addison-Wesley, 1990.
Rothstein, Michael F., Burt Rosner. The professional's guide to
database systems project management. New York: Wiley, 1990.
Rudd, Anthony S. Implementing practical DB2 applications. New York: E
Horwood, 1990.
Rumble, J.R., Jr., and F.J. Smith. Database systems in science and
engineering. Bristol; Philadelphia: Adam Hilger, 1990.
Sayles, Jonathan S. Embedded SQL for DB2: application design and
programming. Wellesley, MA: QED Information Sciences, 1990.
Sayles, Jonathan. SQL for DB2 and SQL/DS application developers.
Wellesley, MA: QED Information Sciences, 1990.
Sayles, Jonathan. SQL spoken here. Wellesley, MA: QED Information
Sciences, 1989.
Schmidt, J.W., S. Ceri, M. Missikoff (edit.) Advances in database
technology, EDBT 88: International Conference on Extending
Database Technology, Venice, Italy, March 14-18, 1988,
proceedings. Berlin; New York: Springer-Verlag, 1988.
Schmidt, Joachim W., Costantino Thanos. Foundations of knowledge base
management: contributions from logic, databases, and artificial
intelligence applications. Berlin; New York: Springer-Verlag,
1989.
Sherif, M.A. Database projects: a framework for effective management.
Chichester, West Sussex, England: E. Horwood; New York: Halsted
Press, 1988.
Shortliffe, E., L. Perrault, G. Wiederhold, and L. Fagan (edit.)
Medical informatics: computer applications in health care.
Reading, MA: Addison-Wesley, 1990.
Siegel, Charles. Mastering FoxPro. San Francisco, CA: Sybex, 1990.
Siegel, Charles. The ABC's of Paradox. San Francisco, CA: Sybex,
1989.
Simpson, Alan. Mastering Paradox. 4th ed. San Francisco, CA: Sybex,
1989.
Slusky, Ludwig. Cases in database design. St. Louis, MO: Times
Mirror/Mosby College Pub., 1988.
Smith, Peter D., G. Michael Barnes. Files and databases: an
introduction. Reading, MA: Addison-Wesley, 1987.
Sosinsky, Barrie. Using FileMaker. Carmel, IN: Que, 1990.
Spooner, D.L., and C. Landwehr (edit.) Database security III, status
and prospects. North-Holland, 1990.
Srinivasan, B., J. Zeleznikow (edit.) Databases in the 1990s:
proceedings of the Australian Database Research Conference,
Melbourne, February, 6, 1990. Singapore; New Jersey: World
Scientific, 1990.
Stanczyk, Stefan K. Theory and practice of relational databases.
London: Pitman, 1990.
Steele, Philip. 66 FoxBASE+ user-defined functions. 1st ed. Blue
Ridge Summit, PA: TAB Books Inc., 1989.
Stonebraker, Michael (edit.) Readings in database systems. San Mateo,
CA: Morgan Kaufmann, 1988.
Storey, Veda Catherine. View creation: an expert system for database
design. Washington, DC: ICIT Press, 1988.
Su, Stanley Y.W. Database computers: principles, architectures, and
techniques. 1st ed. New York: McGraw-Hill, 1988.
Swanson, E. Burton, and Cynthia Mathis Beath. Maintaining information
systems in organizations. Chichester : New York: Wiley, 1989.
Tare, Ramkrishna S. Data processing in the UNIX environment: with
INFORMIX-SQL, Embedded-SQL, C-ISAM, and TURBO. New York: McGraw-
Hill, 1989.
Tasker, Dan. Fourth generation data: a guide to data analysis for new
and old systems. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall, 1989.
Tay, Y.C. Locking performance in centralized databases. Boston:
Academic Press, 1987.
Tenopir, Carol, and Gerald Lundeen. Managing your information: how to
design and create a textual database on your microcomputer. New
York: Neal-Schuman, 1988.
Tenopir, Carol, and Jung Soon Ro. Full text databases. Foreword by
Stephen Harter. New York: Greenwood Press, 1990.
Teorey, Toby J. Database modeling and design: the entity-relationship
approach. San Mateo, CA: Morgan Kaufman, 1990.
Thompson, J. Patrick. Data with semantics: data models and data
management. New York: Van Nostrand Reinhold, 1989.
Towner, Larry E. IDMS/R: a professional's guide to concepts, design
and programming. New York, NY: Intertext Publications, 1989.
Tsai, Alice Y.H. Database systems: management and use. Scarborough,
Ont.: Prentice-Hall Canada; Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall,
1988.
Ullman, Jeffrey D. Principles of database and knowledge-base systems.
Rockville, Md.: Computer Science Press, vol. 1, 1988, vol. 2,
1989.
Vasta, Joseph A. Understanding database management systems. 2d ed.
Belmont, CA: Wadsworth, 1989.
Vidick, Jean-Luc (edit.) Proceedings of the 13th International
Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval.
September 5-7, 1990 in Brussels, Belgium. New York, NY:
Association for Computing Machinery, 1989.
Vinden, Robin J. Data dictionaries for database administrators. Blue
Ridge Summit, PA: TAB Books, 1990.
Vossen, Gottfried. Datenmodelle, Datenbanksprachen und Datenbank-
Management-Systeme. Bonn: Reading, MA: Addison-Wesley, 1987.
Vowell, Jeff D., Jr. DB2: the complete guide to implementation and
use. 2d ed. Wellesley, MA: QED Information Sciences, 1990.
Vuong, Ziep N. IMS/VS data communications programming using message
format service. 1st ed. Blue Ridge Summit, PA: TAB Books, 1990.
Walters, Richard F. Database principles for personal computers.
Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall, 1987.
Wertz, Charles J. The data dictionary: concepts and uses. 2d ed.
Wellesley, MA: QED Information Sciences, 1989.
Whittington, R.P. Database systems engineering. Oxford: Clarendon
Press; New York: Oxford University Press, 1988.
Wiederhold, Gio. File organization for database design. New York:
McGraw-Hill, 1987.
Williams, M.H. (edit.) Proceedings of the seventh British National
Conference on Databases: Heriot-Watt University, July, 12-14,
1989. Cambridge; New York: Cambridge University Press on behalf
of the British Computer Society, 1989.
Winslett, Marianne. Updating logical databases. Cambridge; New York:
Cambridge University Press, 1990.
Wiorkowski, Gabrielle, David Kull. DB2: design & development guide.
2d ed. Reading, MA: Addison-Wesley, 1990.
Wipper, Fritz. Guide to DB2 & SQL/DS. New York: McGraw-Hill, 1989.
Yannakoudakis, E.J. The architectural logic of database systems.
London; New York: Springer-Verlag, 1988.
Yannakoudakis, E.J., and C.P. Cheng. Standard relational and network
database languages. London; New York: Springer-Verlag, 1988.
Zdonik, Stanley, and David Maier (edit.) Readings in object-oriented
databases. San Mateo, CA: Morgan Kaufmann, 1990.


Figure Ref-2. A relational schema for the university
application.